off grid residential solar power systems
Off-grid residential solar power systems are becoming increasingly popular as people seek to reduce their reliance on the traditional power grid and harness the renewable energy of the sun. These systems allow homes to generate, store, and use their own electricity independently of the public grid. Below is an expanded discussion on off-grid residential solar power systems, including their components, benefits, challenges, and considerations for installation.
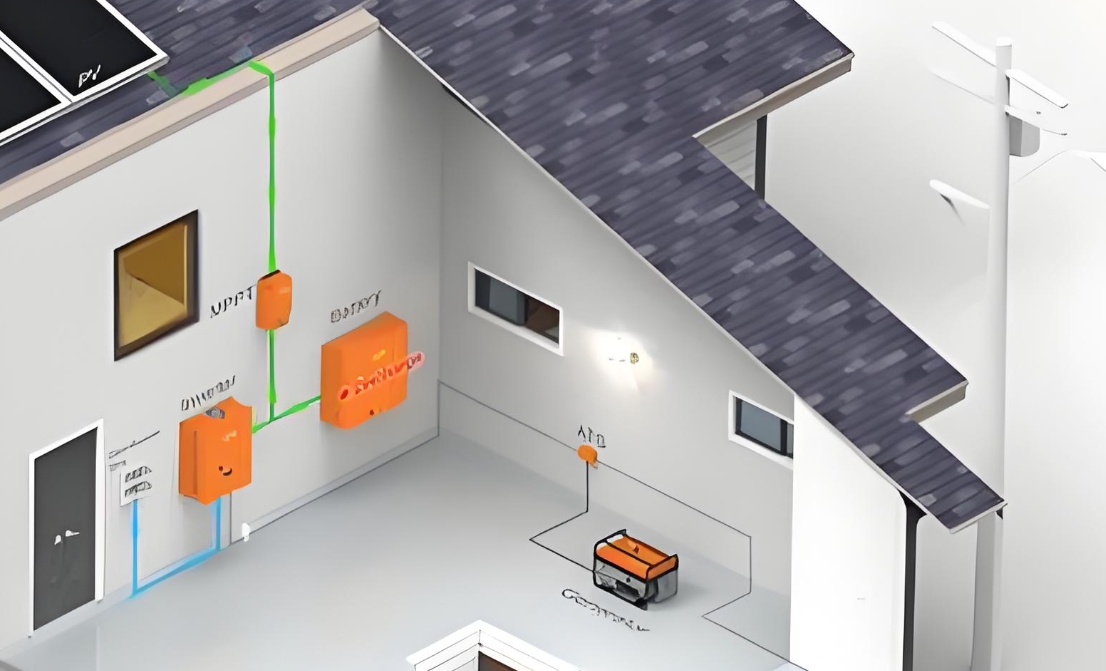
Components of Off-Grid Residential Solar Power Systems
Off-grid solar power systems typically consist of several key components:
Solar Panels: These are the primary component responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. They are usually mounted on rooftops or in open spaces where they can receive maximum sunlight.
Solar Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and protecting the battery from damage.
Batteries: Batteries store the excess electricity generated by the solar panels for use when the sun isn't shining. Off-grid systems usually require a significant battery bank to ensure continuous power supply.
Inverter: The inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity from the batteries into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes.
Backup Generator (Optional): While not strictly necessary, some off-grid systems include a backup generator to provide power during extended periods of bad weather or high energy demand.

Benefits of Off-Grid Residential Solar Power Systems
Energy Independence: Off-grid systems allow homeowners to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on the public grid and potential power outages.
Cost Savings: Over time, off-grid systems can lead to significant savings on electricity bills, especially in areas with high electricity rates.
Environmental Impact: By using renewable energy, off-grid systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Challenges of Off-Grid Residential Solar Power Systems
High Initial Cost: The upfront cost of installing an off-grid system can be significant, including the cost of solar panels, batteries, inverters, and other components.
Maintenance and Monitoring: Off-grid systems require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Limited Energy Storage: Batteries have limited storage capacity, which can be a challenge during extended periods of bad weather or high energy demand.
Considerations for Installation
Energy Needs: Homeowners should carefully assess their energy needs and usage patterns to select the appropriate system size and components.
Location and Climate: The location and climate of the home can affect the performance of the solar panels and the overall efficiency of the system.
Regulations and Permits: Installing an off-grid system may require obtaining permits and complying with local regulations. Homeowners should research the requirements in their area before proceeding with installation.
Professional Installation: Off-grid systems are complex and should be installed by qualified professionals to ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency.
In conclusion, off-grid residential solar power systems offer several benefits, including energy independence, cost savings, and environmental impact. However, they also come with challenges such as high initial cost, maintenance requirements, and limited energy storage. Homeowners considering an off-grid system should carefully assess their energy needs, location, and regulations, and consult with qualified professionals to ensure a successful installation.