residential solar power solutions
Residential solar power solutions are becoming increasingly popular as homeowners seek to reduce their carbon footprint, decrease their energy bills, and take advantage of the abundant renewable energy source that the sun provides. Below is an expanded discussion on residential solar power solutions, exploring their types, benefits, components, and considerations for installation.
Types of Residential Solar Power Solutions
There are several types of residential solar power solutions, each with its own unique set of benefits and applications:
Grid-Tied Systems: Grid-tied systems, also known as on-grid systems, are the most common type of residential solar power solution. These systems are connected to the utility grid and use solar panels to generate electricity. When the sun is shining, the system supplies power to the home and any excess energy is sent to the grid. When the sun isn't shining or the panels are not generating enough energy, the home draws power from the grid.
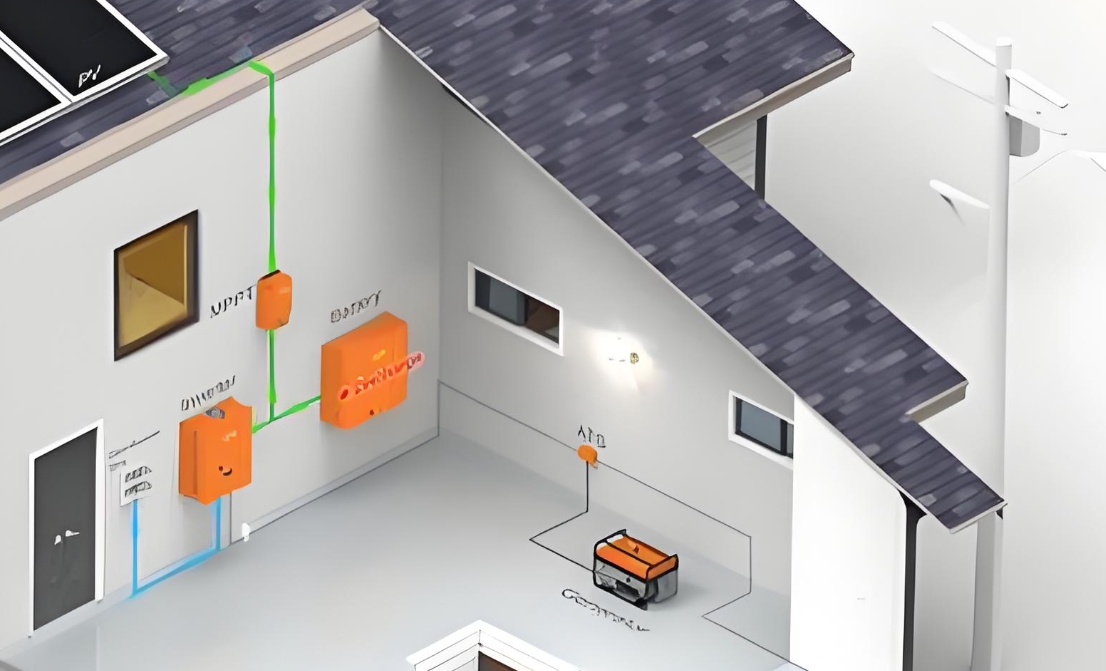
Off-Grid Systems: Off-grid systems are standalone power systems that are not connected to the utility grid. These systems typically include solar panels, a battery bank, and an inverter to convert the DC power generated by the panels into AC power that can be used in the home. Off-grid systems are well-suited for homes that are located in remote areas or that have unreliable grid service.
Hybrid Systems: Hybrid systems combine the benefits of grid-tied and off-grid systems. These systems are connected to the grid but also include a battery bank to store excess energy generated by the solar panels. This allows the home to continue to have power even if the grid goes down, providing a level of energy independence and resilience.
Benefits of Residential Solar Power Solutions
There are several benefits associated with residential solar power solutions, including:
Cost Savings: Solar power can significantly reduce or eliminate a homeowner's electricity bill. Over the lifespan of the system, the savings can be substantial.
Environmental Impact: Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gases or other pollutants. By installing a solar power system, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to the fight against climate change.
Energy Independence: With a solar power system, homeowners can generate their own electricity and reduce their reliance on the utility grid. This can provide a sense of energy independence and resilience, particularly in areas with unreliable grid service.
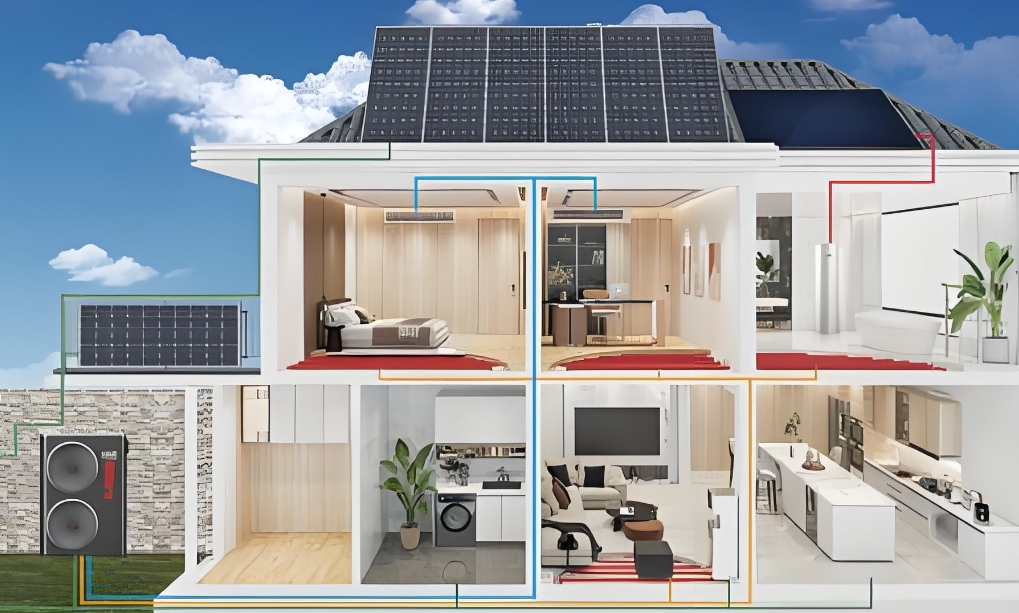

Components of Residential Solar Power Solutions
Residential solar power solutions typically include several key components:
Solar Panels: Solar panels are the primary component of a solar power system. They convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Inverters: Inverters are devices that convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used in the home.
Mounting Systems: Mounting systems are used to secure solar panels to the roof or ground. They should be strong and durable to withstand weather conditions and provide long-term performance.
Batteries (for off-grid and hybrid systems): Batteries are used to store excess energy generated by solar panels. They provide power to the home when the sun isn't shining or the panels are not generating enough energy.
Considerations for Installation
When considering the installation of a residential solar power solution, there are several factors to take into account:
Roof Suitability: The roof of the home should be in good condition and have enough space and the appropriate orientation and tilt to maximize sunlight exposure.
Local Regulations and Incentives: Homeowners should check with their local utility and government agencies to understand any regulations, permits, or incentives that may be required or available for solar power installations.
Cost and Financing: The cost of installing a solar power system can vary depending on the size, type, and components of the system. Homeowners should research financing options and compare costs to ensure that the investment is cost-effective.
In conclusion, residential solar power solutions offer a range of benefits, including cost savings, environmental impact, and energy independence. With careful consideration of the type of system, components, and installation factors, homeowners can make informed decisions about whether a solar power system is the right choice for their home.