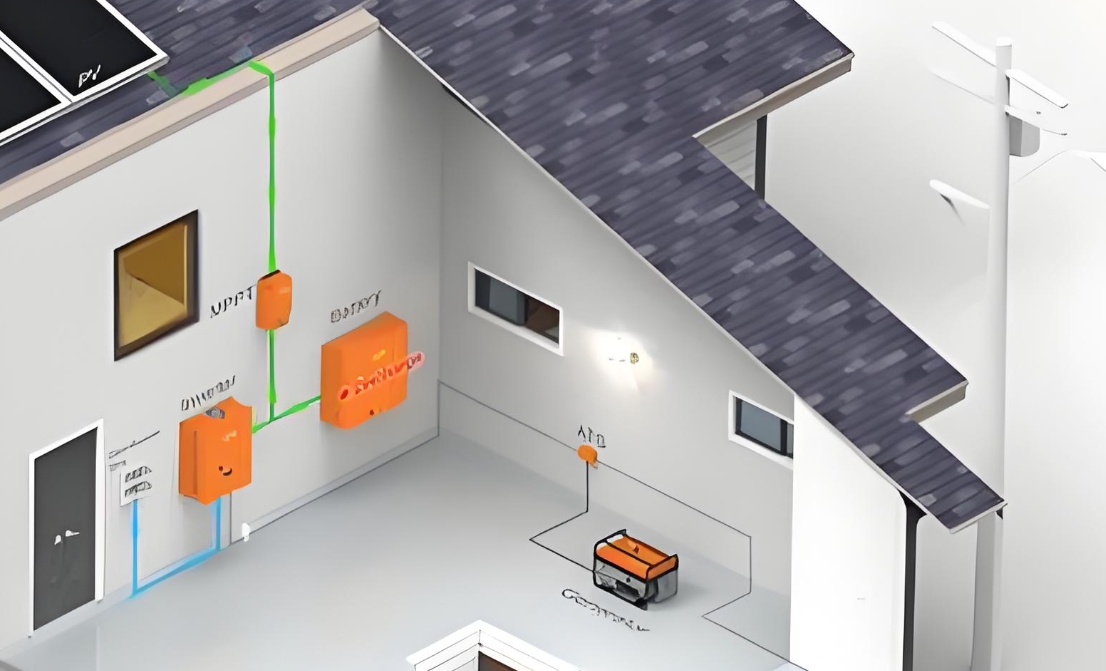
residential backup power systems
Residential backup power systems are essential for ensuring that households remain powered during outages caused by natural disasters, grid failures, or other unforeseen circumstances. These systems provide a reliable source of electricity to critical loads such as lighting, heating, cooling, refrigeration, and medical devices. Here's an expanded discussion on residential backup power systems:

Types of Residential Backup Power Systems
Portable Generators:
Portable generators are compact, easy-to-use devices that provide temporary power. They are fueled by gasoline, diesel, or propane and can be used to power essential household appliances and devices.
While portable generators are affordable and easy to store, they require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure safe and efficient operation. They also produce noise and emissions, which can be a nuisance in residential areas.
Standby Generators:
Standby generators are permanently installed outdoor units that automatically start up when the power goes out. They are fueled by natural gas or propane and can provide continuous power to the entire house or specific circuits.
Standby generators are more expensive than portable generators, but they offer greater convenience and reliability. They are designed to run for extended periods, providing a seamless transition to backup power during outages.
Solar-Powered Backup Systems:
Solar-powered backup systems use solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity is stored in batteries, which can be used to power the home during outages.
Solar-powered backup systems are eco-friendly and can reduce reliance on the grid. However, they may not provide enough power to meet all household needs during prolonged outages, and their effectiveness can be limited by weather conditions.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
Battery energy storage systems use rechargeable batteries to store electricity generated by solar panels, wind turbines, or the grid. When the power goes out, the stored electricity can be used to power essential loads.
BESS systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their flexibility and scalability. They can be tailored to meet specific household needs and can be integrated with renewable energy sources to maximize energy efficiency.
Key Considerations for Selecting a Residential Backup Power System
Power Requirements:
Determine the total power requirements for your home during an outage. Consider the wattage and amperage of the devices and appliances that you need to power and choose a system that can meet or exceed these requirements.
Fuel Source:
Consider the fuel source for your backup power system. Gasoline, diesel, and propane-powered systems require regular fuel refills, while solar-powered and battery-based systems are more sustainable and eco-friendly.
Cost:
The cost of residential backup power systems can vary widely depending on the type, size, and brand. Consider your budget and the potential long-term benefits of each system before making a decision.
Maintenance and Reliability:
Look for systems that are easy to maintain and have a proven track record of reliability. Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your backup power system and ensure that it operates efficiently during outages.
Installation and Permitting:
Check with local utilities and building departments to ensure that your chosen backup power system complies with local regulations and codes. Some systems may require permits or inspections before installation.
Conclusion
Residential backup power systems provide a crucial layer of protection against power outages, ensuring that households remain powered and secure during unexpected disruptions. When selecting a system, consider your power requirements, fuel source, budget, maintenance needs, and local regulations. With the right backup power system in place, you can enjoy peace of mind and continued access to essential services and amenities, even when the grid fails. Remember to consult with professionals to ensure that your system is installed correctly and operates safely and efficiently.